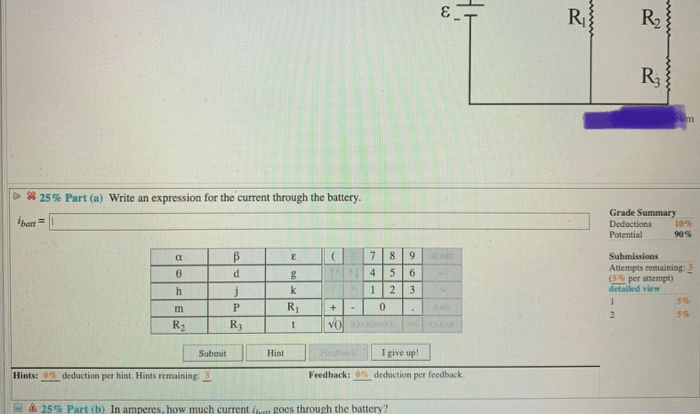
An autotransformer is one of the methods used to transform voltage, offering unique advantages and applications in electrical systems. This article delves into the concept, types, construction, working principle, and practical uses of autotransformers, providing a comprehensive understanding of this essential electrical component.
Autotransformers are a type of transformer that utilizes a single winding to achieve voltage transformation, making them more compact and efficient than conventional transformers. They find widespread applications in industries, power distribution systems, and various electronic devices.
1. Definition of Autotransformers
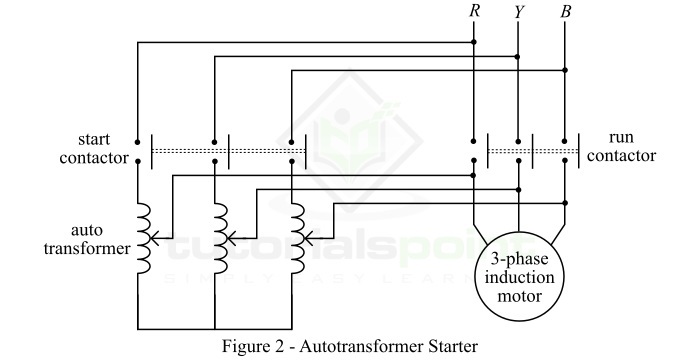
An autotransformer is an electrical transformer that utilizes a single winding to provide voltage transformation. It consists of a coil with multiple taps, allowing for the adjustment of the output voltage. The autotransformer is a cost-effective and efficient solution for voltage regulation and isolation in power systems.
The primary purpose of an autotransformer is to step up or step down the voltage of an alternating current (AC) power supply. By adjusting the position of the tap on the winding, the output voltage can be varied within a certain range.
2. Types of Autotransformers
Autotransformers are classified into two main types based on their construction:
2.1 Variable Autotransformers
- Also known as Variacs, these autotransformers have a continuously adjustable tap, allowing for precise voltage control.
- Variable autotransformers are widely used in laboratory settings and for testing purposes, where precise voltage regulation is crucial.
2.2 Fixed Autotransformers, An autotransformer is one of the methods used to
- Have a fixed tap position, providing a specific voltage transformation ratio.
- Fixed autotransformers are typically used in industrial applications, such as motor starting and voltage stabilization.
3. Construction and Design of Autotransformers
Autotransformers are typically constructed using a single winding made of copper or aluminum. The winding is wound on a laminated iron core, which helps to minimize losses due to eddy currents and hysteresis.
The number of turns in the winding determines the voltage transformation ratio of the autotransformer. A higher number of turns results in a higher voltage transformation ratio.
4. Working Principle of Autotransformers
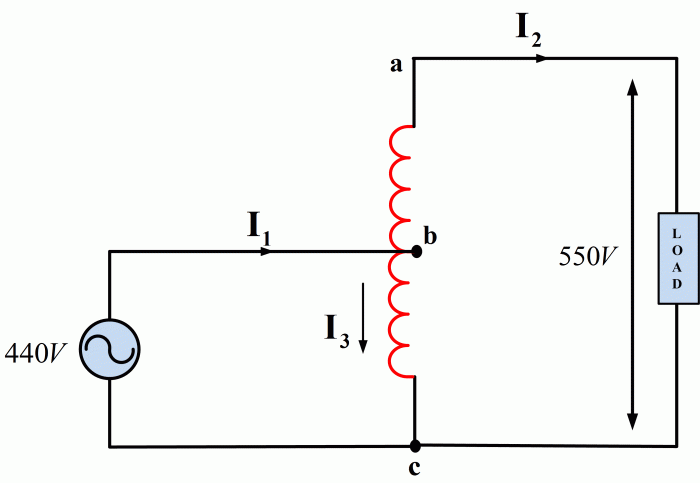
The working principle of an autotransformer is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. When an alternating current flows through the winding, it creates a magnetic field. This magnetic field induces an electromotive force (EMF) in the winding, which is proportional to the number of turns in the winding.
By adjusting the position of the tap on the winding, the number of turns in the primary and secondary windings can be varied. This, in turn, changes the voltage transformation ratio of the autotransformer.
5. Advantages and Disadvantages of Autotransformers
5.1 Advantages
- Compact size and lightweight compared to conventional transformers.
- Cost-effective due to the use of a single winding.
- High efficiency, as there are no additional windings or magnetic circuits.
- Can provide both voltage step-up and step-down transformations.
5.2 Disadvantages
- Limited voltage transformation range.
- Not suitable for isolation applications, as the primary and secondary windings are electrically connected.
- Can be susceptible to overvoltage and short-circuit faults.
6. Applications of Autotransformers
Autotransformers are widely used in various electrical applications, including:
- Voltage regulation and stabilization.
- Motor starting and speed control.
- Phase conversion.
- Testing and laboratory equipment.
7. Comparison with Other Transformer Types: An Autotransformer Is One Of The Methods Used To
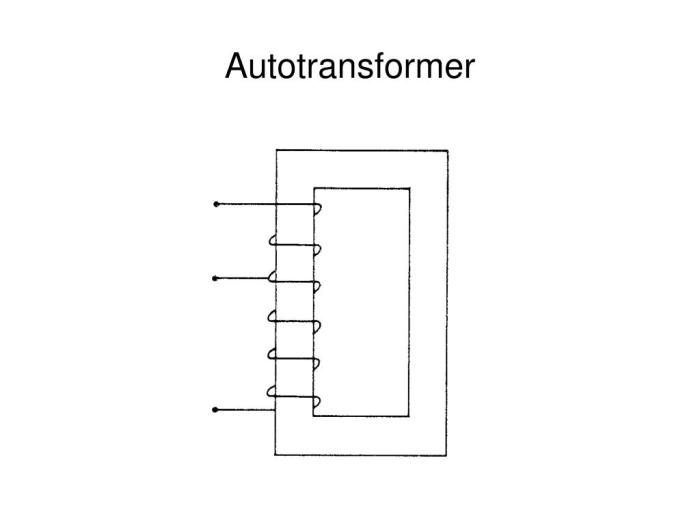
Autotransformers differ from conventional transformers in several aspects:
- Autotransformers use a single winding, while conventional transformers have separate primary and secondary windings.
- Autotransformers have a limited voltage transformation range compared to conventional transformers.
- Autotransformers are more compact and lightweight than conventional transformers.
Question Bank
What is the main purpose of an autotransformer?
An autotransformer’s primary purpose is to transform voltage levels in electrical systems, either stepping up or stepping down voltage as required.
How does an autotransformer differ from a conventional transformer?
Unlike conventional transformers with separate primary and secondary windings, autotransformers utilize a single winding, resulting in a more compact and efficient design.
What are the advantages of using autotransformers?
Autotransformers offer several advantages, including smaller size, lower cost, and higher efficiency compared to conventional transformers.