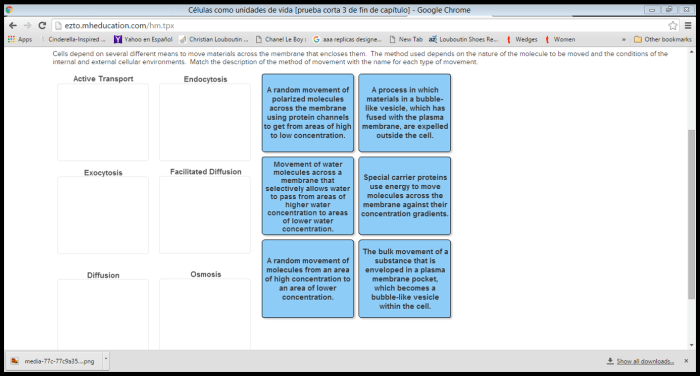
Match the methods of membrane transport with the correct descriptions. – Delving into the fascinating world of membrane transport, this exploration unravels the intricate mechanisms that govern the movement of substances across cellular membranes. From passive diffusion to active transport, we embark on a journey to decipher the key characteristics, types, and energy requirements of these vital processes.
Membrane transport plays a pivotal role in cellular function, facilitating nutrient uptake, waste removal, and signal transduction. Understanding these mechanisms is essential for comprehending the fundamental principles that underpin cellular life.
Membrane Transport Mechanisms
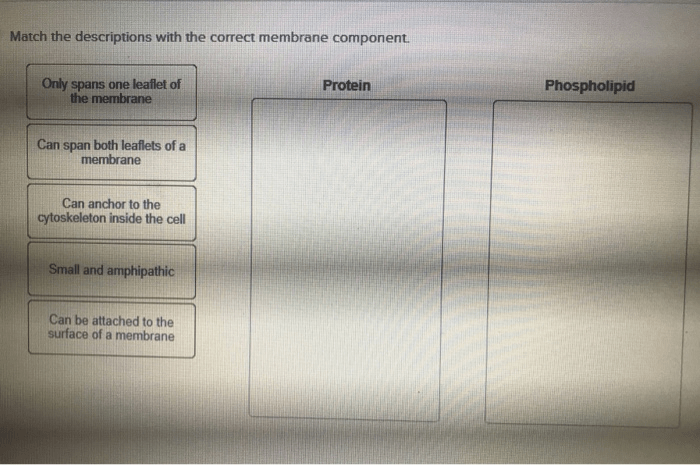
Cell membranes are selectively permeable barriers that regulate the movement of substances into and out of cells. Membrane transport mechanisms facilitate this movement, allowing cells to acquire nutrients, expel waste products, and maintain homeostasis.
Passive Transport
Passive transport is a type of membrane transport that does not require energy input. Substances move down their concentration gradient, from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. Examples of passive transport include diffusion, osmosis, and facilitated diffusion.
Active Transport
Active transport is a type of membrane transport that requires energy input. Substances are moved against their concentration gradient, from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration. Examples of active transport include primary active transport and secondary active transport.
Membrane Transport and Cellular Function, Match the methods of membrane transport with the correct descriptions.
Membrane transport mechanisms play a crucial role in cellular function. They contribute to processes such as nutrient uptake, waste removal, and signal transduction. Disruptions in membrane transport can affect cellular function and lead to various diseases.
Table of Membrane Transport Mechanisms: Match The Methods Of Membrane Transport With The Correct Descriptions.

| Mechanism | Type | Direction of Transport | Energy Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diffusion | Passive | Down concentration gradient | No |
| Osmosis | Passive | Down water concentration gradient | No |
| Facilitated Diffusion | Passive | Down concentration gradient | No |
| Primary Active Transport | Active | Against concentration gradient | Yes |
| Secondary Active Transport | Active | Against concentration gradient | Yes |
Quick FAQs
What is the primary driving force behind passive transport?
Passive transport relies on concentration gradients, with substances moving from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration.
How does active transport differ from passive transport?
Active transport requires energy input to move substances against their concentration gradients, while passive transport occurs spontaneously.
What is the significance of membrane transport in cellular function?
Membrane transport is crucial for nutrient uptake, waste removal, and signal transduction, enabling cells to maintain homeostasis and respond to their environment.