Missing lateral incisors canine substitution – Missing lateral incisors and subsequent canine substitution present a unique challenge in dentistry. This comprehensive exploration delves into the prevalence, causes, and clinical implications of this condition, examining various treatment options and their outcomes.
The absence of lateral incisors, often accompanied by canine substitution, raises concerns regarding aesthetics, function, and occlusion. Understanding the factors contributing to this condition and the available treatment modalities empowers clinicians to provide optimal care for affected individuals.
Missing Lateral Incisors
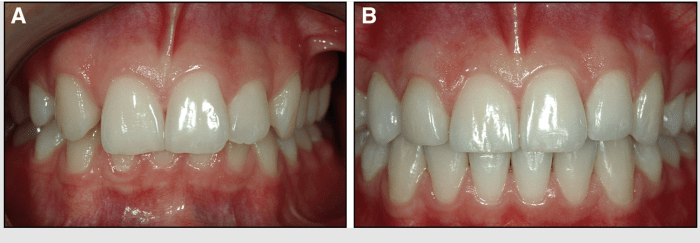
Missing lateral incisors are a common dental anomaly, affecting approximately 2% of the population. The absence of these teeth can be attributed to both genetic and environmental factors.
Genetic Factors
- Mutations in the PAX9 gene have been linked to missing lateral incisors.
- Mutations in the MSX1 gene have also been associated with this condition.
Environmental Factors
- Trauma to the developing tooth bud can lead to missing lateral incisors.
- Exposure to certain medications during pregnancy, such as thalidomide, can also cause this anomaly.
Associated Syndromes, Missing lateral incisors canine substitution
- Missing lateral incisors are a common feature of ectodermal dysplasia.
- They are also associated with cleft lip and palate.
Canine Substitution
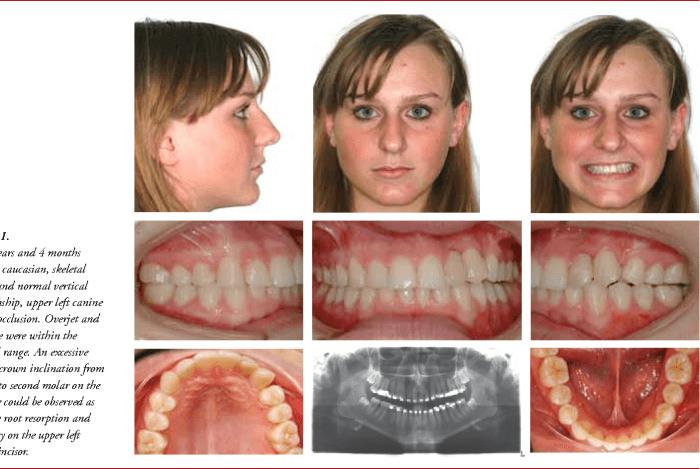
Canine substitution occurs when a canine tooth erupts in the place of a missing lateral incisor. This phenomenon is thought to be caused by the migration of the canine tooth germ into the space left by the missing lateral incisor.
Types of Canine Substitution
- Complete canine substitution:The canine tooth completely replaces the lateral incisor, both in terms of position and function.
- Partial canine substitution:The canine tooth partially replaces the lateral incisor, with the lateral incisor tooth bud present but displaced.
- Pseudo-canine substitution:A premolar tooth erupts in the place of the missing lateral incisor, but it resembles a canine tooth in terms of its shape and size.
Illustrations of Canine Substitution
[Gambar atau ilustrasi yang menunjukkan berbagai jenis canine substitution]
Treatment Options: Missing Lateral Incisors Canine Substitution
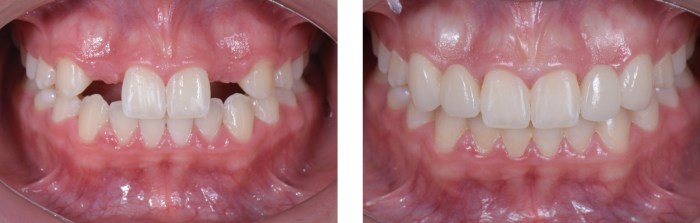
The treatment options for missing lateral incisors include orthodontic treatment, prosthodontic treatment, and surgical treatment.
Orthodontic Treatment
- Orthodontic treatment involves using braces or aligners to move the adjacent teeth into the space left by the missing lateral incisor.
- This option is most suitable for cases of complete canine substitution.
Prosthodontic Treatment
- Prosthodontic treatment involves using a dental bridge or implant to replace the missing lateral incisor.
- This option is most suitable for cases of partial canine substitution or pseudo-canine substitution.
Surgical Treatment
- Surgical treatment involves surgically exposing the impacted lateral incisor tooth bud and moving it into the correct position.
- This option is most suitable for cases where the lateral incisor tooth bud is present but displaced.
Comparison of Treatment Options
| Treatment Option | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Orthodontic Treatment | Conservative, does not require surgery | May take a long time to complete, may not be suitable for all cases |
| Prosthodontic Treatment | Quick and easy to perform, can be used in most cases | May require the preparation of adjacent teeth, may not be as durable as orthodontic treatment |
| Surgical Treatment | Can achieve the most natural-looking results, can be used in cases where the lateral incisor tooth bud is present but displaced | Requires surgery, may be more expensive than other options |
Clinical Implications
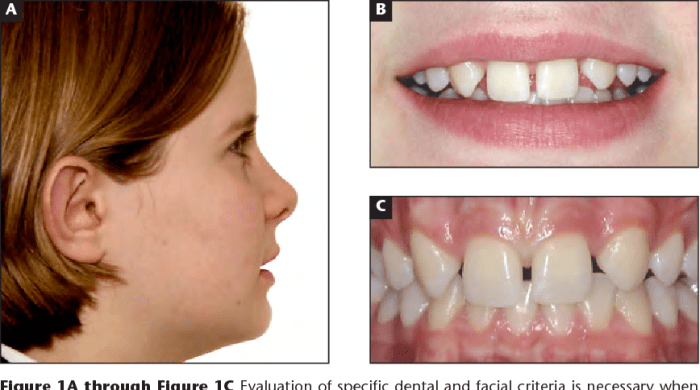
Missing lateral incisors can have a significant impact on dental aesthetics, function, and occlusion.
Dental Aesthetics
- Missing lateral incisors can create a noticeable gap in the smile.
- This can lead to social anxiety and embarrassment.
Dental Function
- Missing lateral incisors can affect the ability to bite and chew.
- This can lead to difficulty eating certain foods.
Dental Occlusion
- Missing lateral incisors can disrupt the normal occlusion of the teeth.
- This can lead to problems such as malocclusion and temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders.
Future Research
There are several areas for future research on missing lateral incisors and canine substitution.
Genetic Studies
- Further research is needed to identify the specific genes and mutations that are responsible for missing lateral incisors.
- This research could lead to the development of genetic tests to predict and diagnose this condition.
Treatment Innovations
- New and innovative treatment methods are needed to improve the outcomes of treatment for missing lateral incisors.
- This research could focus on developing new orthodontic techniques, prosthodontic materials, and surgical procedures.
Long-Term Outcomes
- Long-term studies are needed to investigate the long-term outcomes of different treatment options for missing lateral incisors.
- This research could provide valuable information to help clinicians make informed decisions about the best treatment option for each patient.
Detailed FAQs
What is the prevalence of missing lateral incisors?
Missing lateral incisors are relatively common, affecting approximately 2% of the population.
What are the genetic factors that contribute to missing lateral incisors?
Mutations in genes such as PAX9 and MSX1 have been linked to the development of missing lateral incisors.
What are the different types of canine substitution?
Canine substitution can manifest in various forms, including transposition, rotation, and dilaceration.